C++ static member function
Like static member variable, we can have static member functions.
A member functions that is declared as static has the following properties
1. A static function can have access to only other static members functions or static variables declared in the same class.
2. A static member function can be called using the class name (instead of its objects) as follows
|
class-name:: function-name;
|
Notice The following statement in the program
take the example of the static function displaycount() display the number of objects created till that moment. A count of number of
objects created in maintained by the static variable count
in this example showcode() displays the code number of each object
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
test
{
int code;
count;
:
setcode()
{
count=++count;
}
showcode()
{
std::cout<<"object number" <<code <<"\n";
}
displaycount()
{
std::cout<<"count:" <<count <<"\n";
}
};
test::count;
main()
{
test t1,t2;
t1.setcode();
t2.setcode();
test::displaycount();
test t3;
t3.setcode();
test::displaycount();
t1.showcode();
t2.showcode();
t3.showcode();
0;
}
|
|
count:2
count:3
object number:1
object number:2
object number:3
|
Note :
code=++count;
is executed whenever setcode() function is invoked and the current value of count is assigned to code.
since object has its own copy of code, the value contained in code represents a unique number of its object
Remember This below code not work
|
static void showcount()
{
cout << code;
}
|
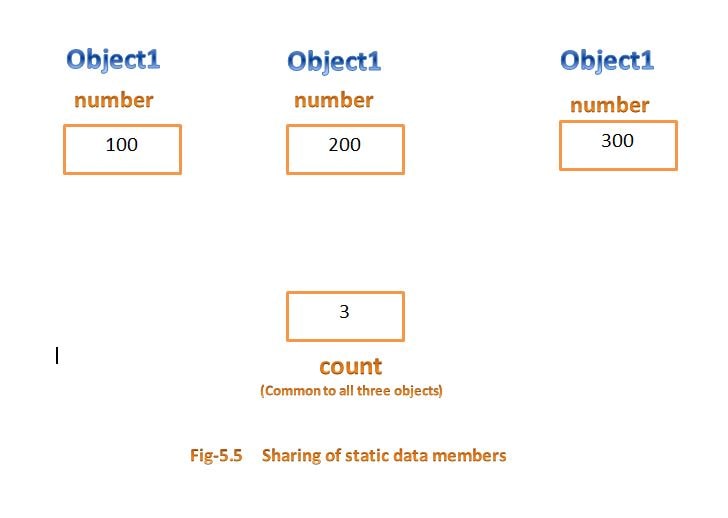
in the below fig show