c++ open using constructor
we learn previous pages about constructor so we know that a constructor is used to initialize an object while it is being created. here the filename is used to initialize the file stream object.
This involves the following steps
1. create first a file stream object to manage the stream using the appropriate class. It is to say the class ofstream is used to create the output stream and the class ifstream to create the input stream
2. Initialize the file object with the desired filename
foe example the following statement open a file named “result” for output
ofstream outfile(“result”); // output only
it is creates outfile as an ofstream object that manages the output stream. This object can be any valid in C++ programming name such as o_file,myfile or fout. This statement also opens the file result
and attaches it to the output stream outfile.
This is in the below fig
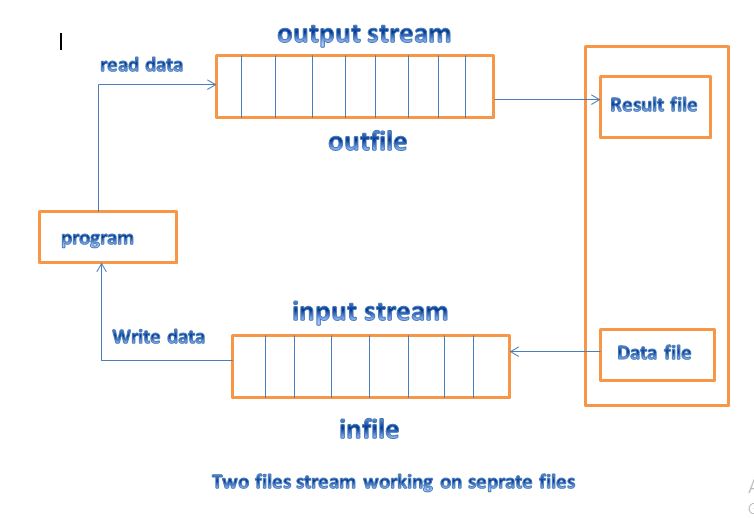
Similarly, in the below the following statement declares infile as an ifstream object and attaches it to the file data for reading(input)
ifstream infile(“data”);
The program may contain statement like
The first method is useful only when we use only one file in the stream. The second method is useful when we want to manage multiple files using one stream
|
outfile<<“Total”;
outfile<
infile>>number;
infile>>string;
|
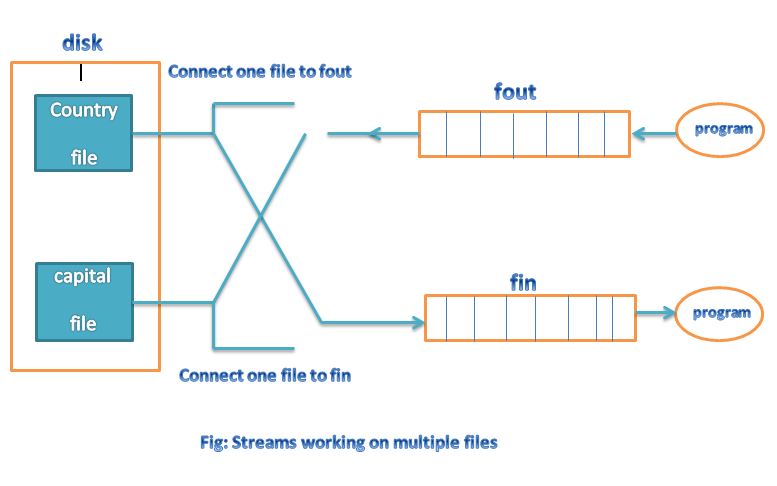
we can use the same file for both reading and writing data as show . The program would contain the following statements
|
program1
…….
…….
ofstream outfile(“salary”);
…..
…..
program2
…….
…….
ifstream infile(“salary”);
……
……
|
The connection with a file is closed automatically when the stream object expires(when the program terminates) In the above statement.
when the program one is terminated, then the salary file is disconnected from the outfile stream same as action takes place when the program2 terminates
Instead of using two programs one for writing data (output) and another for reading data (input) we can use a single program to do both the operations on a file
|
Example
…….
……
outfile.close();
ifstream infile(“salary”);
…….
……
infile.close();
although we have used a single program. we created two file stream objects, outfile(to put data to the file) and infile (to get data from the file).
Note that the use of a statement like
outfile.close();
|
disconnect the file salary from the output stream outfile. Remember the object outfile still exists and the salary file may again be connected to outfile later or to any other stream.
In this example, we are connecting the salary file to infile stream to read data
in the below program uses a single file for both writing and reading the data . First it takes data from the keyboard and writes to the file. after the writing is completed. the file is closed.
The program again open the same file, reads the information already written to it and display the same on the screen
WORKING WITH SINGLE FILE
|
<iostream>
<fstream>
main()
{
std::ofstream outf("ITEM");
std::cout << "Enter item name";
char name[30];
std::cin >> name;
std::cout << name << "\n";
std::cout << "Enter item cost:";
cost;
std::cin >> cost;
outf << cost << "\n";
outf.close();
std::ifstream inf("ITEM");
inf >> name;
inf >> cost;
std::cout << "\n";
std::cout << "Item name:" << name << "\n";
std::cout << "item cost:" << cost << "\n";
inf.close();
}
|
|
out of the above program
Enter ITem name:CD-ROM
Enter item cost:400
Item name:CD-ROM
item cost:250
|