C++ Reference variable
C++ introduces a new kind of variables known as the reference variables
provide a alias(alternative name) for a previously defined variables.
for example, if we make the variable sum a reference to the variable total then sum and total can be used interchangeable to represent that variable or represent the sum . A Example of reference variable is created as follows
Example
|
total=150;
float sum=total;
|
in the above example total is a float type variable that has already been declared. sum is the alternative name declared to representthe variable total. both the variable refer to the same data object in memory. nor the statements
cout << total;
and
cout << sum;
both print the value 150. The statement total=total+15;
will change the value of both total and the sum to 165. likewise, the assigment sum=0; will change the value of both the variable to zero.
A reference variable must be initialized at the time of declaration.This establishes the correspondence between the reference and data object which it names. it is important to note that the initilization of a reference variable is completely different from assignment to it.
c++ assigns additional meaning to the symbol &. here & is not an address operator. The notation float & means reference to float. other example are
|
a[10];
&x=a[10];
&y=’\n’;
|
the variable x is an alternative to the array element a[10]. The variable y is initialized to the newline constant. This created a reference to the otherwise unknown location where the newline constant \n is stored
the variable x is an alternative to the array element a[10]. The variable y is initialized to the newline constant. This created a reference to the otherwise unknown location where the newline constant \n is stored
the following references are also allowed
1. int x;
int *p=&x;
int &m=*p;
2. int &n=50;
the first set of declaration causes m to refer to x which is pointed to by the pointer p and the statement in (2) creates an int object with value 50 and name n.
A major application of reference variable is in passing arguments to functions, consider the folowing
|
f(int &x)
{
x=x+10;
}
main()
{
m=10;
f(m); // f() function call
……..
……..
}
|
where the function call f(m) is executed, the following initialization occurs
int &x=m;
thus x becomes an alias of m after execution the statement
f(m);
let us understand
in the above example , function calls are known as call by reference. this implementation see in the pic . since the variable x and m are alias. when the function increments x,m is also incremented. The value of m becomes 20 after the function is executed. in traditional c, we accomplish this operation using pointers and dereferencing techniques
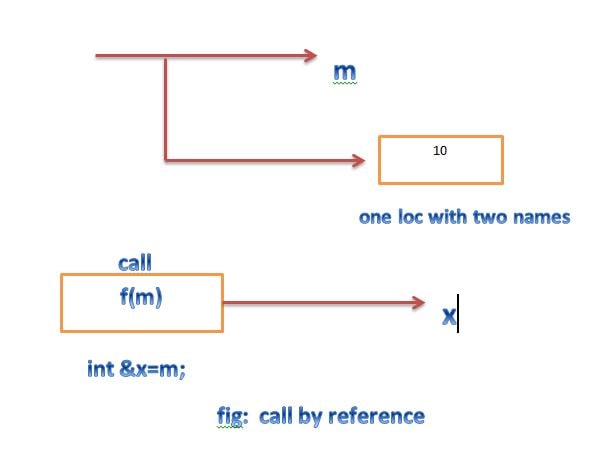
The call by reference mechanism is useful in object-oriented programming because it permits the manipulation of object by reference, and eliminates the copying of object parameters back and forth. it is also important to note . that references can be created not only for built in data types but also for user defined data types such as
structures and classes. references work wonderfully well with these user-defined data types